The last thing you want to read is another “top 10 SEO techniques” list. Not only are most of these “listicles” taken from other sources and then restated, but they have very little substance or credibility to them.
So how is it possible to create an article that lists SEO techniques, but doesn’t fall under this category of content?… Consult the experts of course!
For this article, I reached out to the following marketing practitioners and asked them what internet marketing strategies have been the most effective over the last couple years.
Justin McIntyre — Director of SEO& Content @ Perfect Search Media
Tom Bennet — Head of Product @ Built Visible
Kelly Shelton —VP of Marketing @ Boostability
Adam Heitzman — Managing Partner @ Higher Visibility
Megan Pitcher — Sr. Marketing Specialist @ DriveTime
Jake Bohall — Vice President @ Hive Digital
Everett Sizemore — Director SEO Strategy @ InFlow
Paris Childress —CEO @ Hop Online
Bill Slawski — Director of SEO Research @ Go Fish Digital
Tony Wright —CEO @ WrightIMC
Jim Bader — Senior Director of SEO @ Vertical Measures
Eric Enge —CEO @ Stone Temple Consulting
Although I asked about internet marketing strategies, nearly every marketing practitioner I reached out to mentioned SEO as being a crucial aspect to growing either their businesses or their clients. In light of this, I decided to write an article covering SEO techniques and strategies.
There were a number of techniques and strategies that kept getting mentioned over and over again. There were also some very unique and creative strategies that don’t get talked about, but can be very effective.
The goal of this post is to provide you an overview of what techniques are working when it comes to search engine optimization. Throughout the post, you will find links to excellent resources and guides that provide more in depth information about the particular strategy being covered.
1. In Depth Topic Coverage
Given that pretty much everyone I consulted mentioned SEO as being a high value added marketing practice, it must be pretty important. So for any doubters out there, no SEO is NOT dead! However, it is evolving and with evolution comes change.
Keyword research is one of the first things taught to and is still very effective to this day. However, keyword research is evolving as semantic search and Google’s Knowledge Graph evolves. These technologies allow Google the ability to understand your searches, regardless of how you phrase them. They are by no means perfect (yet), but are getting much better.
Traditionally, when doing keyword research, you try to find keywords with high search volume and low competition. You then build a page targeting this keyword and try to use the keyword throughout your article to emphasize to Google that the page is in fact about that keyword.
This isn’t as necessary anymore.
Instead, Tony Wright of Wright IMC recommends SEO that is centered around a topic, not a keyword. Jim Bader of Vertical Measures also mentioned how his agency has shifted from a hard keyword focus to a visitor focused approach.
At Ahrefs, we use “parent topic,” also known as the highest volume keyword that a page ranks for. If you open up the Ahrefs Keyword Explorer and search for “keyword analysis,” you’ll notice the parent topic is ‘keyword research.”
This means that Google understands that “keyword analysis” and “keyword research” mean pretty much the same thing and ranks the same group of pages for each keyword. “Keyword research” is the more popular search term, so at Ahrefs, we identify it as the “parent topic” for all related searches.
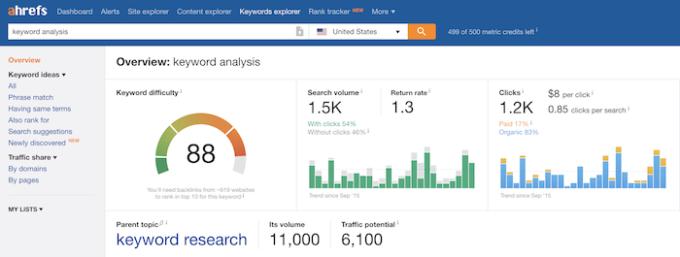
Next, select the parent topic “keyword research” and you’ll be taken to a page that shows other keywords that the #1 result for “keyword research” ranks for.
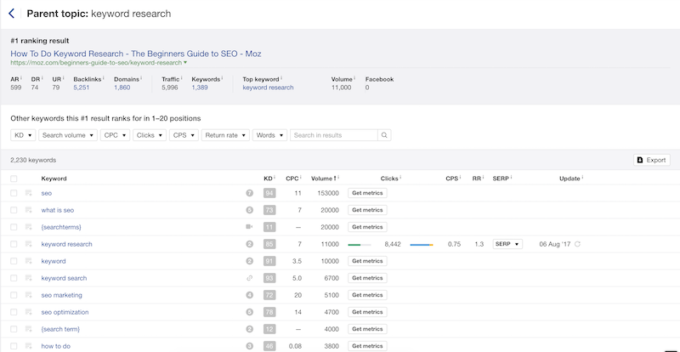
Instead of just trying to stuff a bunch of the keywords you see listed above in your article, you should try to incorporate the underlying topics that they cover. These topics are what Google relates to the parent topic (in this case it is “keyword research”).
You will see much better results if you study your topic and write a comprehensive, in depth article, rather than just trying to incorporate random keywords into an article that is average at best. Use keywords as a guide for what directions to take your writing, not as an end all be all. You will likely end up ranking for hundreds (if not more) of long tail keywords by simply writing a comprehensive piece of content.
2. Re-Optimizing Existing Content
If you are a consistent blogger, or your website is a content creating machine, you may be sitting on an untapped gold mine. Once an article is published, many people simply forget about it and move onto the next one, not realizing the potential of their site’s existing content.
Every once in awhile (quarterly, half-year, annually) you should conduct a content audit on you site. A content audit is an audit where you improve articles, merge them together, or even remove them.
There are hundreds of opportunities for re-optimizing existing content on your site. To ensure this article doesn’t turn into a book, we’ll be covering two strategies that can provide an extremely high return and don’t take too much time to implement
Google Search Console Keyword Optimization
In the “in-depth topic coverage” section above, you learned how to use Ahrefs to build a piece of content by using the “parent topic” and data from pages that rank on page one of the SERPs. Once you publish your new piece of content, you will start accumulating impression data for it in Google Search Console.
More often than not, content is published on a website covering some topic, but without a specific keyword (parent topic) in mind. Even though the content might be well written, it will likely never see the first page of the SERPs because of this shortcoming. The beautiful part about Google Search Console is it shows you what keywords Google is associating with your article. Using this data, you can rewrite your article so that is precisely targets the main topic the keyword(s) encompass.
To find these keywords, first open up Google Search Console. Select “Search Traffic” and then click on “Search Analytics.”
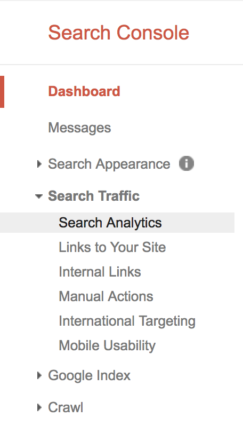
Next, select “Clicks,”“Impressions,”“CTR,” and “Position.” Finally, select “Pages.”
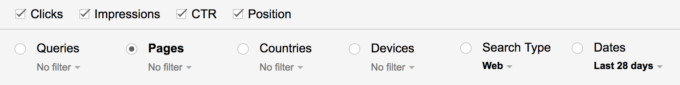
Select the pages you want to optimize. In this case, we will be optimizing a page about the best slackline for beginners.
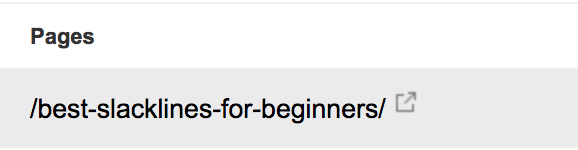
Now, select “Queries” again and the “Pages” option should be filtered for the page that you selected. Filter the keyword results by position and look at keywords that rank between 6 and 20, and that you haven’t extensively written about or mentioned in your article.
For example, the best slackline for beginners article covers information about slacklines, but not about slackline kits. By including information on slackline kits instead of just slacklines, you could improve the page’s rankings for the keyword “best slackline kit.”
![]()
Internal Link Audit and Optimization
An internal link is a link from one page on your site to another. Internal links are beneficial for SEO because they help pass link equity to the page receiving the link. Internal links also make it easier for Google’s crawlers to crawl and index your website. As you create new content on your site, you miss out on internal linking opportunities.
For example, let’s say you wrote a blog post on Monday and then another on Wednesday. The post you wrote on Wednesday could include a link to the post you wrote on Monday. The opposite isn’t necessarily true because you would have to go back into the article you wrote Monday to add a link to the Wednesday article. When you are publishing content on a regular basis, it is difficult to keep up with this type of internal linking.
Depending on how often you publish content on your website, you should conduct an internal link audit every quarter, half year, or year. This type of audit is really easy to do with Google Search Console and a spreadsheet. Here is a link to a pre built spreadsheet template.
Open this and be sure to select File → Make a Copy. Next go to Google Search Console and select “Search Traffic” and then “Internal Links.”
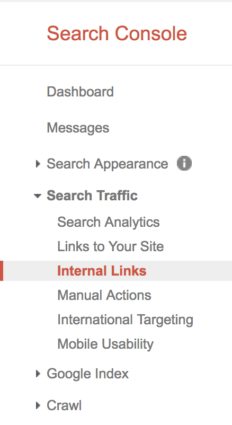
Next, make sure all your website’s URLs are showing and then select “Download this table.”
Download this as a CSV and then copy every URL except your homepage under the “target pages” column.
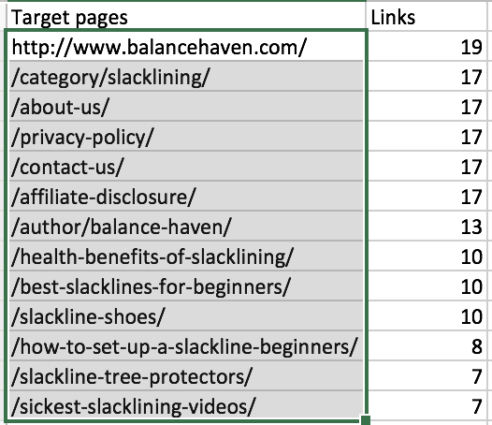
Next, paste the contents into the spreadsheet we provided under the “All Pages On Site” column.

Now go back to GSC and select the page where you want to check the internal links. For this example, we will select the “best slackline for beginners” page.
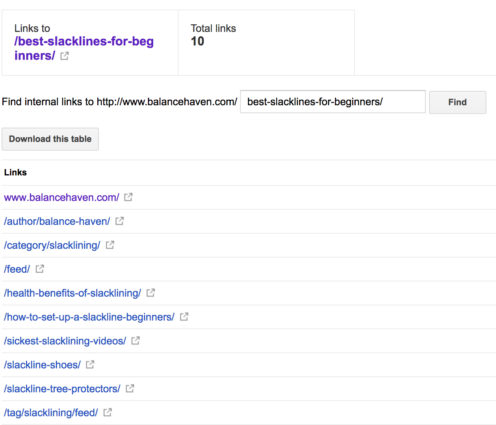
As you can see, there are a total of 10 internal links to this page. Ensure all the page’s internal links are showing and then select “Download this table.” Copy the homepage link found under “Links.” Paste this into cell B1 on the spreadsheet we provided and remove the very last forward slash.
![]()
Now copy every URL in the CSV under the “Links” column except the homepage. Paste these URLs in the spreadsheet we provided under the column titled “Internal Links From Target Page.”
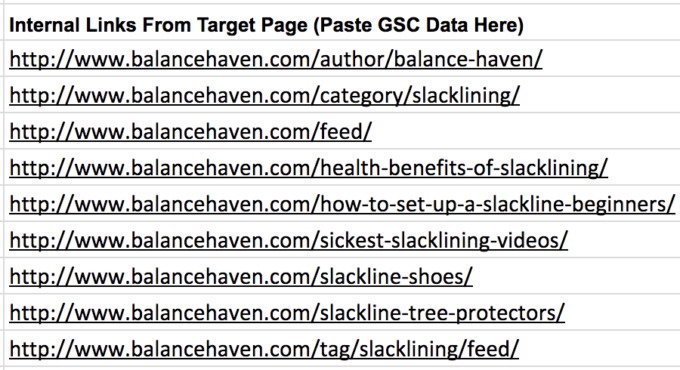
Finally, drag the formulas in column B down until they align with column A.
Now all you do is compare column A with column B. When you see a “No Internal Link” in column B, it means the pages in column A are NOT internally linking to my “best slacklines for beginners” page. Once we decide all the relevant pages are linking to my “best slackline for beginners” page, go through this process again for the next page you want to check for internal links.
3. Linkable Asset Development And Promotion
A linkable asset is a piece of content that does an effective job at attracting backlinks from other websites. Creating and promoting linkable assets is an excellent way to improve your SEO through the acquisition of backlinks. Adam Heitzman has used this strategy over the past few years to grow his agency HigherVisibility.
Development
Developing a linkable asset is fairly straightforward. You simply create a unique, interesting, and useful piece of content for your target audience. Eric Enge of Stone Temple Consulting mentioned how publishing in-depth research studies (aka linkable assets) has helped grow his agency.
There are multiple ways of going about this. Below you will find some great resources and ideas for when it comes to linkable asset development.
Promotion
Once you have created your linkable asset, it’s time to promote it. Promotion really boils down to two strategies:
Outreach: Reaching out to 3rd parties who have audiences that may find your linkable asset useful
Paid promotion: Paying a 3rd party who has an audience that you want to advertise your linkable asset.
4. Redirect Management and 404 Link Reclamation
When an old versions of a website goes through a face lift, the developers working on the site will often change the site’s URL structure. This may occur for structural reason, SEO reasons, or for no reason at all.
Regardless of why the URLs are being changed, Justin McIntyre of Perfect Search Media mentioned how redirect management is crucial. Redirects, specifically 301 redirects, pass the link equity of an old page on a site to a new page. Without redirect management when you are going through a website revamp, you will likely lose your rankings and traffic. For more information on 301 redirects, check out what Google has to say about them.
Let’s say you forget to put a redirect in place when going through a site revamp. The old URL of the page will give visitors a 404 error because they aren’t being redirected. If you find this situation, you definitely want to redirect the URL to a page that is relevant or if none are, the home page. You can use Ahrefs to find 404 pages.
First type in the URL of your site into the search bar at the top. Next, under “Page” select “Best by links.” Finally, select “404 not found” from the filter at the top.
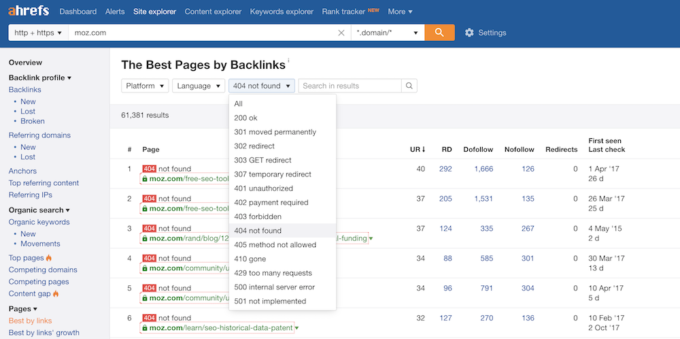
The pages that show up are 404 pages and should have redirects (especially the ones that have any strong RD (referring domains) pointing at them.
5. Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
It’s no secret that we are moving to a mobile first world. Accelerated mobile pages (AMP) are an open source framework for creating lightning fast mobile pages. Paris Childress, CEO at Hop Online, mentioned how he is starting to see the expansion of AMP pages from mostly just article pages, to more complex pages like forms and ecommerce pages.
There are a variety of reasons more and more website owners are adopting AMP, but here are the two big ones for marketers:
- AMP enhances the mobile experience which improves on site metrics like bounce rate
- Google likes sites that load fast and tends to rank faster loading sites higher in the SERPs
To learn more about AMP check out the following resources:
- Project
6. Facebook Advertising and Lookalike Audiences
Most SEOs know the importance of linkable asset development, but don’t use FaceBook ads to promote their linkable assets. If you are a marketer and you haven’t heard of Facebook Advertising, you must have been living under a rock for the past few years. Jake Bohall of Hive Digital mentioned how advertising within social media platforms has been a very effective strategy for growing his and his clients businesses.
Facebook ad campaigns in particular can be extremely effective and the ROI can be massive when done correctly. If you want to learn the basics of Facebook advertising, here is a guide and case study to get you started.
Due to how cheap Facebook ads are, they are awesome for acquiring natural links (as long as your content is link worthy). If you have the budget, the spray and pray method of promoting linkable assets can work very well. You can also be much more specific in who you promote your linkable assets to. For example, you could advertise your content to journalists with the goal of having them mention you.
Once you have a grasp on the basics, you should absolutely check out lookalike audiences on Facebook. Lookalike audiences are audiences that Facebook’s algorithm creates based on a source audience or an audience that you know are your best customers. To learn more about the different types of lookalike audiences you can create, check out this post.
A new(ish) feature surrounding lookalike audiences is value based lookalike audiences. When you are running a business, the ability to target customers who are worth more to you is invaluable because you can better allocate your ad spend on more profitable customers. Value based lookalike audiences provide you this ability. You simply assign a value to different groups of your current customers (your better customers would receive a higher value). Using this data, Facebook’s algorithm will then help you find a similar high-value audience to advertise to.
7. Content Experiments and Personalization
User experience signals are a major SEO ranking factor once your content reaches the first page of Google. Many of the marketing professionals that were contacted for this article mentioned conversion rate optimization (CRO) as a high-value adding marketing activity.
Megan Pitcher mentioned that DriveTime used a multivariate landing page test through Google Analytics Content Experiments that increased leads through their website by 30%.
After seeing these results, she took it a step further and looked at the effects that different messaging (personalization) had on different groups of people. This again dramatically increased conversion rates on the site.
Using Google Analytics Content Experiments is an easy way to test landing pages and can be very impactful to your business’s bottom line. To learn the basics of CRO and Google Analytics Content Experiments, check out the resources below:
Personalization is another buzz word that you will hear a lot in today’s marketing world. It basically means dynamically changing your marketing message (on landing pages, ads, etc.) to connect with each individual customer.
An example of this would be dynamically change the call the action buttons on your site based on the search term the potential customer used to land on your site.
To learn more about personalization and how you can use it to improve your business, check out the resources below.
Final Thoughts
SEO is a fast-paced and forever changing industry. Techniques and strategies that worked 5 years ago can hurt your business nowadays, and some of the best strategies of today weren’t even around 5 years ago.
To stay on top of what is working, it’s important you are always reading, learning, and testing new approaches. One of the best parts about SEO is the willingness to share information in the community. It allows newbies and experts alike to learn from each other, improve their business’, and as a result, advance the SEO industry as a whole.
Now I’d like to ask you, the readers of the Ahrefs Blog; what SEO techniques and strategies are working best for you?
This content was originally published here.